Posterior external arcuate fibers
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
| Posterior external arcuate fibers | |
|---|---|
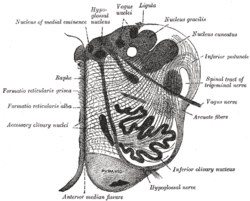
| Diagram showing the course of the arcuate fibers. (Testut.) 1. Medulla oblongata anterior surface. 2. Anterior median fissure. 3. Fourth ventricle. 4. Inferior olivary nucleus, with the accessory olivary nuclei. 5. Gracile nucleus. 6. Cuneate nucleus. 7. Trigeminal. 8. Inferior peduncles, seen from in front. 9. Posterior external arcuate fibers. 10. Anterior external arcuate fibers. 11. Internal arcuate fibers. 12. Peduncle of inferior olivary nucleus. 13. Nucleus arcuatus. 14. Vagus. 15. Hypoglossal. | |
| Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Arcuate fibers labeled at center right.) | |
| Latin | fibrae arcuatae externae posteriores |
| Gray's | subject #187 783 |
| Dorlands/Elsevier | f_05/12361829 |
The posterior external arcuate fibers (dorsal external arcuate fibers) take origin in the gracile and cuneate nuclei; they pass to the inferior peduncle of the same side.
It is uncertain whether fibers are continued directly from the gracile and cuneate fasciculi into the inferior peduncle.
The term "cuneocerebellar tract" is sometimes used to collectively refer to the posterior external arcuate fibers.[1]
Contents[hide] |
[edit] See also
[edit] References
[edit] Additional images
[edit] External links
- NeuroNames hier-793 - dorsal external arcuate fibers
- NeuroNames hier-800 - cuneocerebellar tract
| This neuroscience article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained herein may be outdated. Please edit the article if this is the case, and feel free to remove this notice when it is no longer relevant.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Posterior_external_arcuate_fibers"
Personal tools
Interaction
- This page was last modified on 8 May 2007, at 02:18.
- All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License. (See Copyrights for details.)
Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a U.S. registered 501(c)(3) tax-deductible nonprofit charity.
- Privacy policy
- About Wikipedia
- Disclaimers